AminoWeed 56 Booster effect Starter N 9 - 56% amino acids
Amino acids are essential to the nutrition of all living organisms as they constitute the structural units of proteins (amino acid chains).
Amino acids are found in the cells and intercellular fluids of plants and play an essential role in many physiological processes, such as growth, development, and fruit formation, or when frost, drought, or other abiotic stresses have altered the plant's ability to synthesize.
AminoWeed is an organic nitrogenous biostimulant with a very high amino acid content obtained by enzymatic hydrolysis. This balanced amino acid complex (nutri amino acid complex) is directly assimilated by the plant. 56% of amino acids, this high rate gives AminoWeed a great quality and a strong reactivity:
- Relaunch of the protein and carbohydrate metabolism (neo-glucogenesis).
- Improves the synthesis of precursors of plant resistance and protection (glutathione,...).
AminoWeed stimulates the resistance and the growth of plants, its action is very fast thanks to an immediate foliar and root assimilation.
Its action is targeted on the revival of crops at the beginning of the cycle, during production and in stressful situations.
AminoWeed is recommended for the correction of nitrogen deficiencies (Starter effect), for the revival of growth and production of crops, for the activation of soils and substrates and for the improvement of the resistance of plants in stressful situations (cold soils, wet soils, frost, water stress...)
Use
1 to 2ml/L. In foliar spraying, for the starting stage and during the culture, and for the revival in situation of stress, 2 to 3 applications at 8-10 days of interval. In watering, drip, sprinkling, according to the needs.
Composition: Organic nitrogen = 9% (110g/L) 56% amino acids of which 25% free. 50% organic matter.
UAB Usable in organic agriculture in application of the EC regulation n° 834/2007.
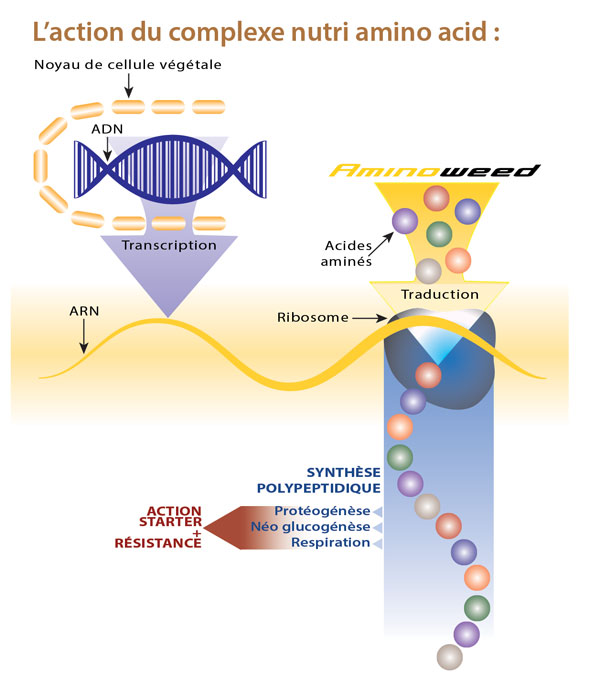
The action of the nutri amino acid complex :
List of essential amino acids for plants:
 Alanine: has an action on the speed of growth of plants and stimulates the formation of chlorophyll. This amino acid is one of the early products of photosynthetic carbon dioxide fixation. It also stimulates root development and is the main amino acid in the sap.
Alanine: has an action on the speed of growth of plants and stimulates the formation of chlorophyll. This amino acid is one of the early products of photosynthetic carbon dioxide fixation. It also stimulates root development and is the main amino acid in the sap.
Arginine: active in the stimulation of photosynthesis and delays the senescence process. Has an action on the speed of the vital processes and on the strength of resistance of the plant against diseases, stresses, ....
Aspartate: has an action on the strength of resistance of the plant against diseases, stress,... It represents a source of nitrogen for the plant and participates in many metabolic processes. Aspargin is the most important amino nitrogen transporter in the plant.
Cysteine: has an action on the reduction of sulfur in the plant. Participates in the assimilatory reduction of sulfate in the chloroplasts. It serves as a "gateway" for reduced sulfur in all organic molecules, as glutamate is for reduced nitrogen. From cysteine, all other sulfur compounds in the cell are derived, especially methionine and glutathione.
Glutamate: has an action on the vegetative growth from the beginning of the vegetative growth until the harvest. Promotes the assimilation of inorganic nitrogen by the plant. It is a precursor of new amino acids. Glycine: is one of the first compounds used in the synthesis of chlorophyll (prevention of chlorosis). Has a crucial action in the formation of plant tissues. It contributes to the vegetative growth of the plant and has a role in the pollination process and fruiting. Has an important chelating effect. It acts on the development of buds and leaves. It is also involved in resistance systems in the face of adverse situations.
Histidine: has an action on the vegetative growth from the beginning of the vegetative growth until the harvest. It is involved in a large number of metabolic processes: cell production, production of histamine.
Isoleucine: has an action on the vegetative growth from the beginning of the vegetative growth until the harvest.
Leucine: has an action on vegetative growth from the beginning of vegetative growth until harvest. Helps to regenerate and repair cell tissues. Regulates nitrogen levels in the plant.
Lysine: active in the stimulation of photosynthesis and delays the senescence process. Has an action on the vegetative growth from the beginning of the vegetative growth until the harvest. It is also involved in resistance systems in the face of adverse situations.
Methionine: has an action on the maturity of fruits and has an important role in the revitalization of roots. Acts on the senescence of leaves and flowers and delays the abscission of leaves and fruits. Participates in the metabolism of sulfur. It is a very important plant phytohormone.
Phenylalanine: is at the origin of phenolic acids, flavonoids, gluconisates, alkaloids, suberins and lignins which play an essential role in the defense mechanisms and in the constitution of walls and fibers. Promotes the germination of shoots and stimulates rooting.
Proline: has an action on the management of water for the cultures and it reinforces the cellular walls (osmoprotector). It has an action on the resistance to extreme conditions such as heat, cold, drought, salinity. It favors the pollination rate, by protecting the pollen against unfavorable temperatures or by favoring the resumption of pollen germination after the cold.
Serine: has an action on the stimulation of photosynthesis. Has an action on the strength of resistance of the plant against diseases, stress, .... Has an important role in the hormonal balance in the plant. Has an action on the reduction of sulfur. Precursor to cysteine, sulfur amino acid. Participates in the assimilatory reduction of sulfate in the chloroplasts.
Threonine: has an action on the strength of resistance of the plant against diseases, stresses, ....
Tryptophan: has an action on the strength of resistance of the plant against diseases, stress,... Is a main precursor of indole acetic acid, the most important plant growth substance of the auxin group. It is synthesized mainly in the stems and young leaves, as well as in the developing seeds. Main effects: growth, cell elongation, apical dominance, stimulation of fruit development, bud formation, new root formation, stimulation of ethylene synthesis, inhibition of leaf and fruit abscission.
Tyrosine: has an action on the resistance strength of the plant against diseases, stress,... Is at the origin of phenolic acids, flavonoids, gluconisates, alkaloids, suberins and lignins which play an essential role in the defense mechanisms and the constitution of walls and fibers.
Valine: has an action on the speed of root formation and on the speed of plant growth. It also has an action on the formation of seeds. It is also involved in resistance systems in the face of adverse situations.













 Alanine: has an action on the speed of growth of plants and stimulates the formation of chlorophyll. This amino acid is one of the early products of photosynthetic carbon dioxide fixation. It also stimulates root development and is the main amino acid in the sap.
Alanine: has an action on the speed of growth of plants and stimulates the formation of chlorophyll. This amino acid is one of the early products of photosynthetic carbon dioxide fixation. It also stimulates root development and is the main amino acid in the sap.