Reflectors MH - HPS
What is a reflector?
Reflectors optimize your lighting and limit losses. They are to be used with CFL, HPS or MH bulbs.
Neon, T5 are already equipped with internal reflectors. As for the leds there is no need for reflectors. You can nevertheless intensify the light with mylar coating.
Reflectors are essential for the reverberation of light, they allow to target the lumens on the plants. The shape of the reflector determines the distribution of the light and the heat released. Closed reflectors concentrate the light flow better. The materials generally used are bright or hammered aluminum.
The advantage of hammered aluminum is that it disperses the luminous flux in dozens of directions, which avoids heating points.
They are all equipped with E40 sockets, for all MH, HPS, hybrid and CFL lamps from 125 to 300W. Remember to buy the necessary cables for the socket-ballast / ballast-mains connections.
Intensity = number of lumens emitted at the source squared by the distance.
The distance between lamps and plants is very important and should not be approximated, because every centimeter counts.
Several factors intervene in the evaluation of this distance: surface and shape of the reflector, size of the growing room, aeration, intensity of the bulb...
The shape of the reflector and its coating determine the distribution of the light, as well as the presence of unwanted hot spots. Glazed reflectors, Light rails and Spreaders are used to avoid these harmful hot spots for the leaves.

Find our complete catalog of reflectors or pre-designed kits of reflectors and their CFL or HPS/MH bulbs on Culture Indoor.
How to calculate the right distance between plant, light and reflector?
STEP 1: calculate the size of the grow room.
So the first thing you need to do is to measure it accurately: calculate the total volume of the greenhouse in cubic meters. You will need the length, width and height of the grow room.
Use the simple formula:

Length (m) x Width (m) x Height (m) = Volume of greenhouse effect (m³) A x B x H = V(m³)
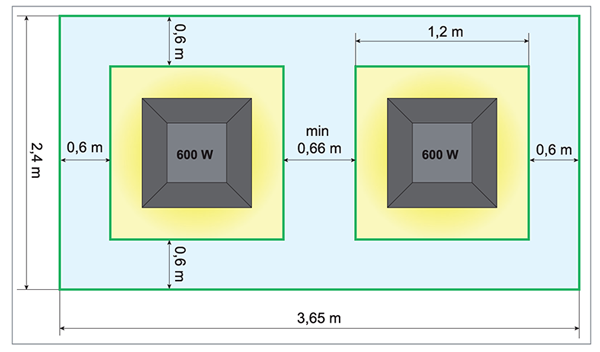
For example, your greenhouse has the following dimensions: length (A) - 3.65 m, width (B) - 2.4 m, height (H) - 2.5 m (Fig. 1).
Total volume (m³) = 3.65 x 2.4 x 2.5 = 21.9 m³
In addition, a well-insulated room can be more easily monitored
STEP 2: Selecting lighting equipment
Once you know the size of the room, calculate the best way to light it. Your mission is to provide your plants with all the light they need to grow and thrive, while maintaining an optimal environment for plant metabolism in your indoor garden.
NOTE! Be aware of the safety distances of horticultural lamps. This means that if you have a low ceiling height, you should consider using the lower wattage lights. For example, the room should have a ceiling height of 2 m so that you can use the 600 W lamps.
 |
The recommended distance between the light and the canopy. |
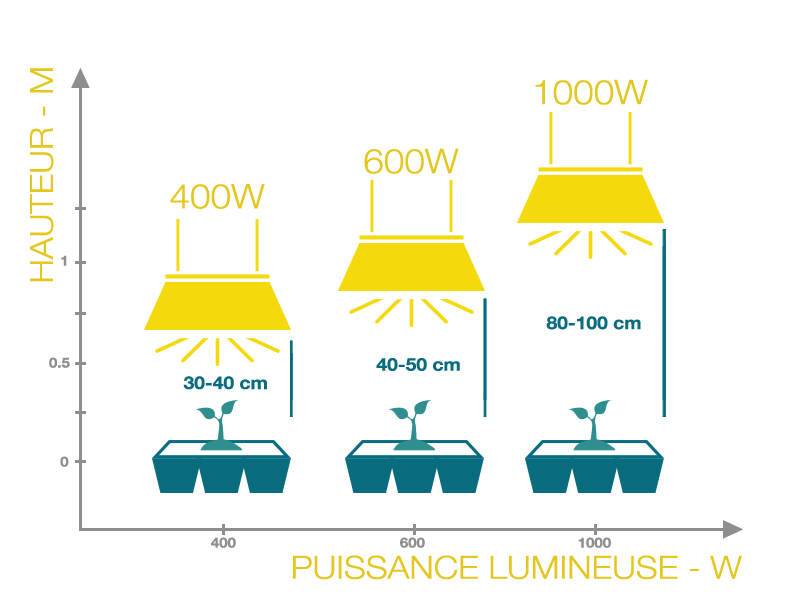 |
The most commonly used light wattages for indoor growing are: 1000W, 600W, 400W and 250W. |
|
|
Each light has a defined space. |
|
|
Fig. 2. the minimum distance between plants should not be less than 0.66 m. Experienced growers can choose much more space than that. In our example we use 2 x 600 W lights (fig. 3). |
|
|
Fig. 3: Grow a room with W 2x600 lamps. Example of a room of 2.4 x 3.65 m equipped with two 600W lamps. |
|
|
Fig. 4: Room with 6x600W lamps. Example of a room of 2.4 x 3.65 m, equipped with two 600W lamps. |
NOTE! Keep in mind that the above information is for lamps mounted horizontally in normal conditions with open or closed reflectors. If you are using parabolic reflectors with vertically mounted lamps or aircooled reflectors you can afford to bring the light closer to the plants by using ventilated, glazed reflectors like Xtracool, Monster Warrior, Cooltube...
So the available floor space in the room is 3,65 mx 2,4 m. You can try to squeeze as much light as possible into this room, but keeping in mind practicality if you want an easy and comfortable room you will need adequate access around your plants to make maintenance and inspections easy. About 0.66m around your plants is a good working area.
Light distribution
Below is a schematic illustration of the concentration of lumens depending on the shape of the reflector. In red, you can see that some reflectors are more efficient in reflecting a maximum of lumens (red area).